Okada M, Egan CA, Heeren TFC, Tufail A, Fruttiger M, Maloca PM. Retina. 2018 Jan;38 Suppl 1:S97-S104. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001812.
PURPOSE:
To investigate retinal microcystoid spaces in macular telangiectasia type 2 with spectral domain optical coherence tomography.
METHODS:
Retrospective review of 135 patients enrolled in the MacTel Natural History Observation and Registry Study at Moorfields Eye Hospital, United Kingdom. One hundred seventy-two eyes from 86 patients who had a comparable scan protocol of at least 30 μm interval were included for analysis. Retinal microcystoid spaces were identified and segmented and metrics analyzed.
RESULTS:
From 172 eyes of 86 patients, microcystoid spaces were found in 11 eyes (6.4%) from 8 patients (9.3%). The mean number of microcystoid spaces per eye was 12.9 ± 18.2. Most were located in the inner nuclear layer. The inferonasal quadrant of the macula was the least commonly affected region. Microcystoid spaces were distributed entirely within the assumed macular telangiectasia area on blue light reflectance in all but 2 eyes (4 of 142 microcysts). The median diameter of the microcystoid spaces was 31 μm (range 15 μm-80 μm).
CONCLUSION:
Microcystoid spaces as a phenotype of macular telangiectasia should be considered in the differentials for microcystic edema. Understanding the pathogenesis of these lesions may provide further insight into the role of Müller cell dysfunction in this disorder.
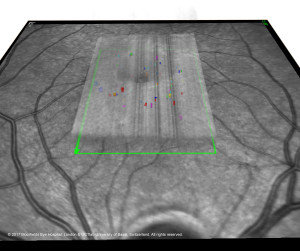
Segmentation of microcysts in MACTEL TYPE 2. In a central OCT volume (shown as semi-transperent area; Heidelberg Spactralis, Heidelberg, Germany), multiple microcystic lesions are segmented that are shown as colored spaces. © 2017 Moorfields Eye Hospital, London, and OCTlab University of Basel, Switzerland. All rights reserved.
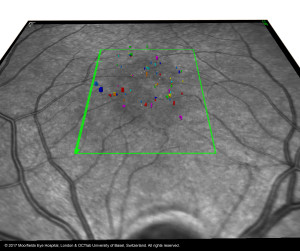
Segmentation of microcysts in MACTEL TYPE 2. Same image as shown previously but full transparence of obtained OCT retina volume. The microcystics lesions are typically distributed in a central zone (“MACTEL zone”). © 2017 Moorfields Eye Hospital, London, OCTlab University of Basel, Switzerland. All rights reserved.
